OECD forecasts a sharp economic slowdown and higher inflation in the U.S., citing tariffs
 Economic Impact of U.S. Tariffs on 2025-2026: A OECD Forecast
Economic Impact of U.S. Tariffs on 2025-2026: A OECD ForecastThe OECD has issued a critical assessment of the current global economic landscape, forecasting a significant economic slowdown and higher inflation in the United States, particularly influenced by U.S.-China trade tensions. This forecast is encapsulated within their outlook for the year 2025-2026, where they emphasize the impact of tariffs on the U.S.'s economy.
### The Slowdown: U.S. Economic Growth Perspective
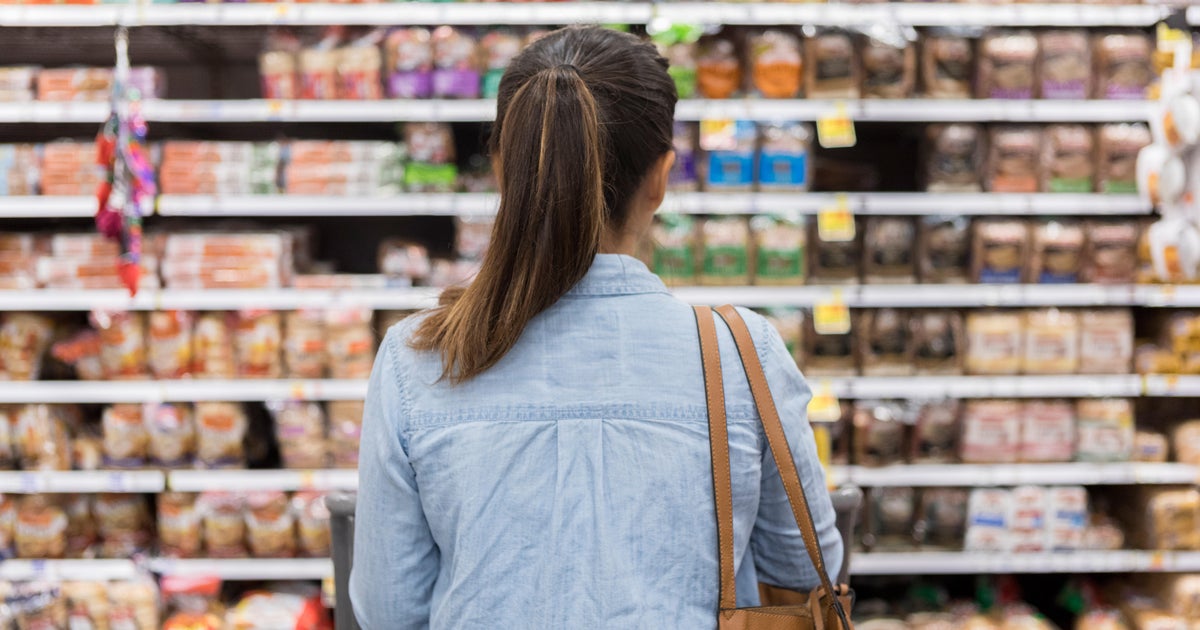
The OECD projects a "nearly markedly" slowdown in U.S. economic growth during this period. This is attributed to ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions and the uncertainty surrounding President Donald Trump's administration. The U.S., as the world's largest import country, will face substantial supply disruptions due to China's retaliatory tariffs on its products. These tariffs are expected to increase price gaps in key sectors such as food and clothing, leading to higher costs for consumers.
### Higher Inflation: Implications for Consumers and Businesses
The forecast highlights that inflation is likely to rise significantly, with average price increases exceeding those seen in 2023. This includes a marked increase in prices for essential goods like food and clothing. The U.S. economy will experience slower growth over multiple quarters or years, affecting labor markets and business operations.
### Impact on the Labor Market
The increased costs from tariffs could strain employment as wages may decline, particularly among workers in sectors where trade barriers are significant, such as agriculture and steel. This situation might lead to lower productivity and a shift toward more flexible work arrangements, potentially replacing traditional jobs with remote or hybrid workforce roles.
### Influence on Business Operations
U.S. companies will likely face rising costs when responding to the tariffs, impacting their ability to export goods effectively. This could strain international trade balances, particularly in sectors where U.S. dominance is significant, such as automotive and electronics.
### Household Budgeting: Consumer Uncertainty
The higher prices and supply issues may lead to increased household budgeting uncertainty. Consumers might save less or face greater spending uncertainty, potentially reducing demand for essential goods. This uncertainty could exacerbate economic uncertainty overall, affecting demand and economic growth.
### Public Policy Considerations
Policy responses must consider the complexity of trade relations. The OECD suggests exploring other solutions, such as dialogue and trade agreements, rather than solely reacting to tariffs. Mutual respect is crucial to avoid prolonged conflicts and promote a more stable economic environment.
### Conclusion: Collaboration for Stability
While avoiding prolonged conflicts in global trade remains challenging, it is essential for U.S. policymakers and nations involved to collaborate. This cooperation will likely lead to more stable growth, ensuring mutual benefit and reducing the risk of further conflicts. The OECD's forecast serves as a cautionary guide, highlighting the urgency of cooperation to safeguard global economic stability.
------
Topic Live